Start » Pistachio psylla: A threatening pest in crops in Castilla-La Mancha and Extremadura
Pistachio psylla: A threatening pest in crops in Castilla-La Mancha and Extremadura
Table of Contents
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
Pistachio nuts in Spain
The presence of pistachio psylla in Spain has been confirmed in fourteen municipalities in the regions of Castilla-La Mancha and Extremadura. This pest, native to the Middle East and the eastern Mediterranean, represents a threat to pistachio crops in our country. Details about the presence of this pest in the aforementioned municipalities are described below, as well as its description, the damage it causes and the difficulties in its control.
Presence of the plague in municipalities of Castilla-La Mancha and Extremadura
The presence of pistachio psylla has been detected in fourteen municipalities located in Castilla-La Mancha and Extremadura. This pest has managed to establish itself in these areas, which represents a concern for farmers in the region.
Description of pistachio psyllids
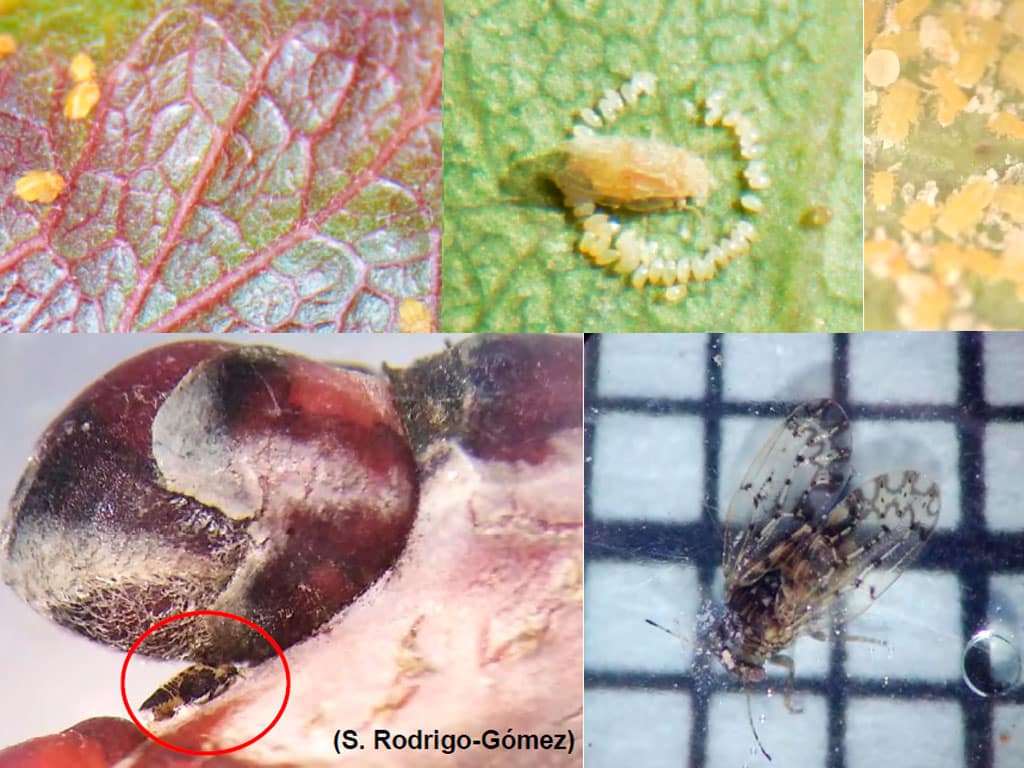
Pistachio psyllids are sucking insects belonging to the psyllid family. These insects are small and have two pairs of membranous wings. They have a length that varies between 1.2 and 1.8 mm. The females deposit their eggs on the underside of young leaves, and the yellowish-orange nymphs secrete a cottony mass composed of whitish waxes.

Damage caused by the presence of pistachio psylla
The presence of pistachio psylla can cause various damages to crops. Among them, leaf yellowing, leaf curling, necrosis, premature defoliation of the tree, drop of flower buds and the appearance of saprophytic fungi stand out. These damages can seriously affect the production and quality of pistachio fruits.
Vulnerable stages of the pest and difficulties in its control
The most vulnerable stages of the pest are the nymphs, however, their location on the underside of the leaves makes their control difficult. This represents a challenge for farmers, who find it difficult to use phytosanitary products to combat the pest. It is important to visually monitor the nymphs and cottony masses to detect and control the presence of pistachio psyllae.
Prevention and control measures
Given the presence of pistachio psylla in crops in Castilla-La Mancha and Extremadura, it is essential to implement prevention and control measures to prevent the spread of this pest. Below are various strategies that can be used:
Cultural measures to control the pest
- It is recommended to maintain biodiversity in the plantations, promoting the presence of hedge species on the edges of the plots that act as a refuge for natural predators of pistachio psylla and vegetal covers in the cultivation streets whenever water conditions allow it.
- If the pest occurs in isolated outbreaks, it is important to regularly wash the foliage of the trees with a solution of liquid soap, vinegar and water, which helps eliminate the cottony masses and reduce the presence of nymphs.
Physical and chemical treatments as control alternatives
- For effective control of pistachio psylla, physical treatments can be used such as the application of yellow sticky traps, which attract adult insects and capture them, thus reducing their population.
- Likewise, the use of phytosanitary treatments with authorized products permitted for this crop is recommended, which must be applied in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions, respecting the established safety intervals and avoiding flowering times so as not to affect pollinators. Some recommended products are mineral oil, azadirachtin or imidacloprid.
- In the field of organic farming, treatments with pyrethrins can also be used, an insecticide of natural origin that is effective for pest control.
Importance of conserving the pest's natural enemies
The natural enemies of pistachio psyllae, such as some predatory insects and parasitoids; Ants, wasps, lacewings or ladybugs play a fundamental role in its biological control. Therefore, it is essential to preserve and encourage the presence of this auxiliary fauna in crops. To achieve this, it is recommended to avoid the indiscriminate use of insecticides that may affect these beneficial organisms.
Pistachio psylla and its impact on crops
Pistachio psylla have reached Spain, specifically to fourteen municipalities in Castilla-La Mancha and Extremadura, generating concern for crops in this region. Its presence has been detected mainly in Pistacia terebinthus rootstocks, used in the cultivation of pistachios, and in isolation in the Pistacia vera variety once grafted.
Presence in rootstocks of Pistacia terebinthus and Pistacia vera
The detection of pistachio psylla in Pistacia terebinthus rootstocks has been alarming, since these insects can cause various damages to crops. However, it has been found that its appearance in Pistacia vera, after the grafting process, has been very rare. Although its current impact on pistachio plantations in the peninsula is not significant, it is important to be attentive to its possible spread and effects in the future.
Monitoring and correct identification recommendations
Given the presence of pistachio psylla, it is crucial to constantly monitor the detected populations. Furthermore, it is essential to have a correct identification of the pest, since there are other insects and diseases that can cause similar symptoms in pistachio crops. In this way, appropriate control measures can be implemented to minimize the impact of the pest.
Research on the biology and control of the pest
The presence of pistachio psylla in Spain is considered unexpected, which raises the need to carry out continuous research on its biology and control. It is essential to know more about the life cycles, reproduction habits and feeding preferences of these insects to develop effective control strategies and mitigate their impact on pistachio crops.
Prevention and actions to avoid future problems
Prevention is key to avoid future problems caused by pistachio psylla. It is recommended to maintain biodiversity in plantations, as this can help reduce the presence of the pest. Likewise, it is important to conserve and encourage the natural enemies of pistachio psyllae, such as predators and parasites, which can help control their population naturally. Furthermore, it is necessary to continue researching and developing control alternatives, both physical and chemical, that are effective and respectful of the environment.
Sources:
- Guide to integrated pest management of pistachio (Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries, Food and Environment)
- A study confirms the presence of the pistachio psyllid in Spain (Phytoma.com)
- Pests in the pistachio tree (CIAG – IRIAF).https://chaparrillo.castillalamancha.es/sites/default/files/2021-07/Pistacho_PLAGAS_2021_CIAG.pdf

Related content:

Pests of the pistachio tree: The green stink bug (Nezara viridula L.)

Alternaria in the pistachio tree: how to prevent and treat this common disease.

Rust in the pistachio tree: Pileolaria terebinthi C. and its impact

Septoriasis in the pistachio tree: Causes, symptoms and control measures.
Seeker:
Find out now:
You may also like:

Pistachios star in the new pyramid of the Mediterranean Diet, one of the healthiest in the world.



Pruning the pistachio tree: a key aspect in the cultivation and growth of the plant.
Entries by category:
Share this post with one click:
